Examples of anaerobic organisms include: Glucose + electron acceptors (other than o2) → lactic acid / ethanol + 2 atp molecules.
20 Min What Does Anaerobic Respiration Mean In Biology For Girls, What is the meaning anaerobic respiration? Aerobic, or respiration in the presence of oxygen, and anaerobic, or respiration without oxygen.
 18.1 Glycolysis a level biology student From alevelbiologystudent.weebly.com
18.1 Glycolysis a level biology student From alevelbiologystudent.weebly.com
What is the meaning anaerobic respiration? Glycolysis, in which glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvic acid (pyruvate) in the general cell cytoplasm. End products are co2 and water. What is the meaning anaerobic respiration?
18.1 Glycolysis a level biology student A type of cell respiration that takes place in anaerobes, and in which energy is released from glucose and other foods without the presence of oxygen.
Aerobic respiration is a continuous process and it happens all the time inside the cells of animals and plants. In this case, an atom other than oxygen is the. It is shown by several anaerobic bacteria, yeasts, protozoans, helminths, and even animal cells. More detailed differences between the two are as follows:
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
Of, relating to, or being activity in which the body incurs an oxygen debt. Therefore, this type of cellular respiration does not use oxygen to produce energy. Anaerobic respiration occurs in human muscles and in red blood cells where there are no mitochondria. They will not participate in the tca cycle or the ets. Anaerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary.
 Source: cancercelltreatment.com
Source: cancercelltreatment.com
Anaerobic respiration is the metabolic process in which oxygen is absent, and only the stage of glycolysis is completed. [adjective] living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen. Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy. Fermentation is another name for this process. Anaerobic Vs Aerobic Do You Have Pathogens? Why?.
 Source: lactate.com
Source: lactate.com
Most of the plant and animal cells use aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is a continuous process and it happens all the time inside the cells of animals and plants. A type of cell respiration that takes place in anaerobes, and in which energy is released from glucose and other foods without the presence of oxygen. In addition to lactic acid fermentation. Lactate testing for triathlon training, why does every athlete want a.
 Source: biology.stackexchange.com
Source: biology.stackexchange.com
In this case, an atom other than oxygen is the. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, whereas anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. In addition to lactic acid fermentation. It is shown by several anaerobic bacteria, yeasts, protozoans, helminths, and even animal cells. biochemistry How does the body switch between aerobic and anaerobic.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
In aerobic respiration complete oxidation of glucose takes place. The primary difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration is the presence or absence of oxygen during the processes. The overall reaction of anaerobic respiration of a glucose molecule can be expressed as follows; In this process, pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis is directly reduced by lactic acid dehydrogenase enzyme to form lactic acid. Cellular Respiration.
 Source: wasfa-hd.blogspot.com
Source: wasfa-hd.blogspot.com
[adjective] living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen. Like other anaerobic organisms, anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen for respiration. In anaerobic respiration, the glucose molecule is incompletely oxidized. During respiration, oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor at the end of an electron transport chain, which is why aerobic organisms must breathe air containing oxygen in order to survive. Where Is The Energy Stored In Atp Quizlet Wasfa Blog.
 Source: biology.stackexchange.com
Source: biology.stackexchange.com
They will not participate in the tca cycle or the ets. (of an organism or tissue) living in the absence of air or free oxygen. This series of biochemical reactions is also called a “metabolic pathway.” two types of cellular respiration exist: Anaerobic respiration occurs in human muscles and in red blood cells where there are no mitochondria. cellular respiration How is NAD+ used in lactic acid fermentation.
 Source: tessshebaylo.com
Source: tessshebaylo.com
The respiration can be aerobic, which uses glucose and oxygen, or. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, whereas anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. In addition to lactic acid fermentation. Glycolysis is the first stage of respiration, in which a glucose molecule is broken down into two pyruvate molecules. Word And Chemical Equation For Anaerobic Respiration Tessshebaylo.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
What is anaerobic respiration | physiology | biology | fuseschoolsometimes animals and plants cannot get enough oxygen to respire aerobically, such as during. The overall reaction of anaerobic respiration of a glucose molecule can be expressed as follows; Most of the plant and animal cells use aerobic respiration. Aerobic, or respiration in the presence of oxygen, and anaerobic, or respiration without oxygen. Aerobic Bacterial Metabolism Definition & Process Video & Lesson.
![[28+] Schematic Diagram Meaning Definition [28+] Schematic Diagram Meaning Definition](https://i2.wp.com/www.biologyonline.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/anaerobic-respiration-definition-denitrification-and-schematic-diagram.jpg) Source: vespa-trike-scooter.blogspot.com
Source: vespa-trike-scooter.blogspot.com
In this process, pyruvic acid produced in glycolysis is directly reduced by lactic acid dehydrogenase enzyme to form lactic acid. Of, relating to, or being activity in which the body incurs an oxygen debt. Fermentation is another name for this process. The respiration can be aerobic, which uses glucose and oxygen, or. [28+] Schematic Diagram Meaning Definition.
 Source: biodifferences.net
Source: biodifferences.net
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, whereas anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration is a form of respiration that does not require oxygen and can occur in animals, plants and other microorganisms. Aerobic respiration is more efficient than. Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy. Difference between Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Bio Differences.
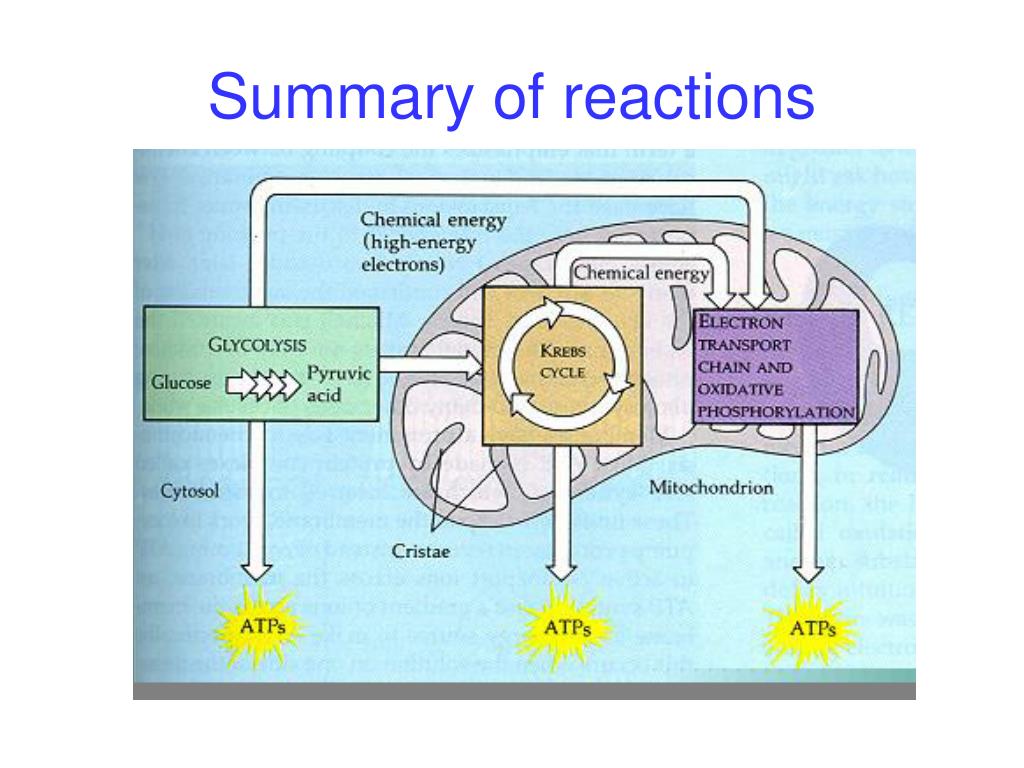 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, whereas anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. In anaerobic respiration, the glucose molecule is incompletely oxidized. Like other anaerobic organisms, anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen for respiration. Lactic acid fermentation is the anaerobic breakdown of glucose into the lactic acid it occurs in lactic acid bacteria, some fungi and muscle cells. PPT Biology 3A respiration PowerPoint Presentation ID6264960.
 Source: biologydictionary.net
Source: biologydictionary.net
[adjective] living, active, occurring, or existing in the absence of free oxygen. Glycolysis, in which glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvic acid (pyruvate) in the general cell cytoplasm. Respiration is a chemical reaction which takes place in all livings cells and releases energy from glucose. A type of cell respiration that takes place in anaerobes, and in which energy is released from glucose and other foods without the presence of oxygen. Aerobic Respiration The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary.
 Source: tessshebaylo.com
Source: tessshebaylo.com
End products are co2 and water. Cellular respiration is defined as the conversion of fuel into energy and nutrients within the mitochondria and cytosol of cells. A type of cell respiration that takes place in anaerobes, and in which energy is released from glucose and other foods without the presence of oxygen. Glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy. Balanced Chemical Equation For Anaerobic Respiration In Animals.
 Source: alevelbiologystudent.weebly.com
Source: alevelbiologystudent.weebly.com
Respiration is a chemical reaction which takes place in all livings cells and releases energy from glucose. Anaerobic respiration occurs in human muscles and in red blood cells where there are no mitochondria. The reactions fall into two stages: A type of cell respiration that takes place in anaerobes, and in which energy is released from glucose and other foods without the presence of oxygen. 18.1 Glycolysis a level biology student.
 Source: education-portal.com
Source: education-portal.com
Aerobic respiration is a continuous process and it happens all the time inside the cells of animals and plants. In addition to lactic acid fermentation. Aerobic respiration is more efficient than. Like other anaerobic organisms, anaerobic bacteria do not require oxygen for respiration. Anaerobic Bacterial Metabolism Definition & Process Video & Lesson.
 Source: humanbiology.pressbooks.tru.ca
Source: humanbiology.pressbooks.tru.ca
However, anaerobic organisms use either fermentation or anaerobic cellular respiration to produce atp. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, whereas anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. On the other hand, anaerobic bacteria, yeast cells, prokaryotes, and muscle cells perform anaerobic respiration. During rigorous exercise, the anaerobic respiration response leads to the production of lactic acid within muscle cells, which facilitates the production of atp, helping to provide additional energy. 4.11 Anaerobic Processes Human Biology.

Fermentation is another name for this process. In anaerobic respiration, the glucose molecule is incompletely oxidized. This series of biochemical reactions is also called a “metabolic pathway.” two types of cellular respiration exist: It is shown by several anaerobic bacteria, yeasts, protozoans, helminths, and even animal cells. What Is The Definition Of Cellular Respiration In Biology SHOTWERK.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
What does the term anaerobic mean in biology? A type of cell respiration that takes place in anaerobes, and in which energy is released from glucose and other foods without the presence of oxygen. Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place. Aerobic respiration is a continuous process and it happens all the time inside the cells of animals and plants. Respiration & gas exchange.
 Source: opencurriculum.org
Source: opencurriculum.org
The reactions fall into two stages: Glycolysis, in which glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvic acid (pyruvate) in the general cell cytoplasm. During rigorous exercise, the anaerobic respiration response leads to the production of lactic acid within muscle cells, which facilitates the production of atp, helping to provide additional energy. This occurs in microorganisms, but is also a temporary response to oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration ‹ OpenCurriculum.
 Source: tessshebaylo.com
Source: tessshebaylo.com
This occurs in microorganisms, but is also a temporary response to oxygen. What is anaerobic respiration | physiology | biology | fuseschoolsometimes animals and plants cannot get enough oxygen to respire aerobically, such as during. Most of the plant and animal cells use aerobic respiration. 1.it takes place in the absence of oxygen. What Is The Word And Balanced Symbol Equation For Anaerobic Respiration.
 Source: sullivan1990.blogspot.com
Source: sullivan1990.blogspot.com
Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place. It is shown by several anaerobic bacteria, yeasts, protozoans, helminths, and even animal cells. In aerobic respiration complete oxidation of glucose takes place. The overall reaction of anaerobic respiration of a glucose molecule can be expressed as follows; Sulli's Biology Ch 9 Respiration and Fermentation.
 Source: documents.pub
Source: documents.pub
Pertaining to or caused by the absence of oxygen. This series of biochemical reactions is also called a “metabolic pathway.” two types of cellular respiration exist: It only occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. In this case, an atom other than oxygen is the. 7.4 Anaerobic Respiration Cellular Respiration. Anaerobic Respiration.
 Source: shotwerk.blogspot.com
Source: shotwerk.blogspot.com
The primary difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration is the presence or absence of oxygen during the processes. However, anaerobic organisms use either fermentation or anaerobic cellular respiration to produce atp. Aerobic, or respiration in the presence of oxygen, and anaerobic, or respiration without oxygen. This series of biochemical reactions is also called a “metabolic pathway.” two types of cellular respiration exist: What Is Cellular Respiration Mean In Science SHOTWERK.
 Source: byjus.com
Source: byjus.com
Glycolysis is the first stage of respiration, in which a glucose molecule is broken down into two pyruvate molecules. Pertaining to or caused by the absence of oxygen. What does the term anaerobic mean in biology? This series of biochemical reactions is also called a “metabolic pathway.” two types of cellular respiration exist: Aerobic And Anaerobic Respiration Major Differences.
In Aerobic Respiration Complete Oxidation Of Glucose Takes Place.
Pertaining to or caused by the absence of oxygen. The reactions fall into two stages: What is the meaning anaerobic respiration? Glycolysis, in which glucose is converted to two molecules of pyruvic acid (pyruvate) in the general cell cytoplasm.
[Adjective] Living, Active, Occurring, Or Existing In The Absence Of Free Oxygen.
The reactions fall into two stages: Actinomyces, clostridium, propionibacterium, bifidobacterium, bacteroides fusobacterium etc. Aerobic, or respiration in the presence of oxygen, and anaerobic, or respiration without oxygen. Examples of anaerobic organisms include:
Aerobic Respiration Requires Oxygen, Whereas Anaerobic Respiration Takes Place In The Absence Of Oxygen.
However, anaerobic organisms use either fermentation or anaerobic cellular respiration to produce atp. Aerobic respiration is more efficient than. Aerobic respiration is a continuous process and it happens all the time inside the cells of animals and plants. End products are co2 and water.
In This Case, An Atom Other Than Oxygen Is The.
Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place. The primary difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration is the presence or absence of oxygen during the processes. Lactic acid fermentation is the anaerobic breakdown of glucose into the lactic acid it occurs in lactic acid bacteria, some fungi and muscle cells. In addition to lactic acid fermentation.







