These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. It is made up of two different kinds of tissues the xylem and phloem.
15 Min What Are 2 Types Of Vascular Tissue Ideas, What are the two types of vascular tissues? Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves.
 Plants by Lily Parker From haikudeck.com
Plants by Lily Parker From haikudeck.com
The two types of vascular tissue are xylem and phloem. The vascular tissue system is composed of two different types of tissues: The xylem is a complex tissue containing a range of cell types including: Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves.
Plants by Lily Parker Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves.
What are the two types of vascular tissue? Vascular tissue is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, the main transport systems of plants. Vascular tissue is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, the main transport systems of plants. 2.3 vascular tissues and cell types there are two vascular tissues in the vascular tissue system:
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Xylem is responsible for the transport of water and dissolved ions from the roots upwards through the. It consists of a series of elements that form tubes throughout the plant. What are the two types of vascular tissues? These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. PPT Vascular Tissue Xylem and Phloem PowerPoint Presentation ID.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. Xylem is to take the water from the root system to the leaves, and phloem is to take the food from the source (being the area of photosynthesis or storage) to all other parts of the plant. The two types of vascular tissue, xylem and phloem, are responsible for moving water, minerals, and the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant. Xylem, which conducts water and nutrients up from the roots, and phloem, which distributes food from the leaves to other parts of the plant. PPT Seedless Vascular Plants PowerPoint Presentation ID5882103.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
They are the conducting tissues that are responsible for the transport of water, mainly the xylem, while the transport of food in plants is done by the phloem tissue. Vessel cells, tracheids, fibers, parenchyma. Vascular tissue is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, the main transport systems of plants. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. Botany 2Plant Vascular Tissue YouTube.
 Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
Source: digitalatlasofancientlife.org
What are the two types of vascular tissue in. The two types of vascular tissue are xylem and phloem. Dermal tissue is composed of epidermal cells, closely packed cells that secrete a waxy cuticle that aids in the prevention of water loss. Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves. Introduction to Vascular Plant Structure Digital Atlas of Ancient Life.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Although both xylem and phloem form a continuous tissue system throughout the plant body, the two tissues have different functions. The two types of vascular tissue are xylem and phloem. The cells in vascular tissue are typically long and slender. Different types of stele are: biodiversity of plants.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The two types of vascular tissues xylem and phloem. Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves. It consists of a series of elements that form tubes throughout the plant. They are the conducting tissues that are responsible for the transport of water, mainly the xylem, while the transport of food in plants is done by the phloem tissue. Stem Growth Biology for Majors II.
 Source: ybstudy.com
Source: ybstudy.com
What are the two types of vascular tissue in. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. What are the 3 types of tissues found in vascular plants? The two types of vascular tissue, xylem and phloem, are responsible for moving water, minerals, and the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant. Difference between Xylem and Phloem with Similarities.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. Xylem is responsible for the transport of water and dissolved ions from the roots upwards through the plant. What are the two types of vascular tissue in plant? Vascular tissue.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. By berries emulous of fame grand (151k points) asked in biology jan 3, 2021 24 views. Plants have only three tissue types: What are the two types of vascular tissue in plant? Plant cell, Microscopic photography, Microscopic cells.
 Source: plantscience4u.com
Source: plantscience4u.com
Peripheral vascular disease (pvd), commonly known as peripheral artery disease or pad is a blood circulation disorder of the arteries and veins situated away from your heart and brain. The cells in vascular tissue are typically long and slender. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. They are the conducting tissues that are responsible for the transport of water, mainly the xylem, while the transport of food in plants is done by the phloem tissue. Types of Vascular Bundles in Plants Plant Science 4 U.
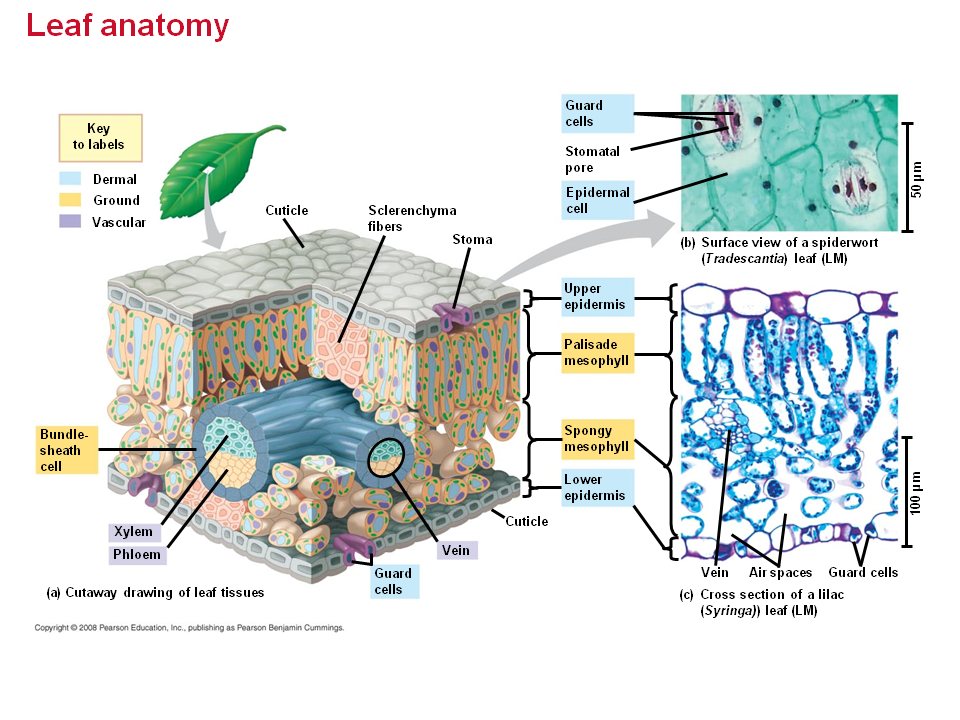
Stele originated & evolved in pteridophytes. Vascular tissue is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, the main transport systems of plants. What are the two types of vascular tissue? Plants are a kingdom of living organisms which can carry out carbon fixation. The Vascular Cambium and Secondary Vascular Tissue.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
They are the conducting tissues that are responsible for the transport of water, mainly the xylem, while the transport of food in plants is done by the phloem tissue. Xylem is responsible for the transport of water and dissolved ions from the roots upwards through the. Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves. What are the two types of vascular tissue in. Organization of plant vascular tissues. a Appearance of the provascular.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Peripheral vascular disease (pvd), commonly known as peripheral artery disease or pad is a blood circulation disorder of the arteries and veins situated away from your heart and brain. Vascular tissue types exist in the form of vascular bundles. Vascular tissue is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, the main transport systems of plants. Vascular tissue is a complex conducting tissue, formed of more than one cell type, found in vascular plants. Tissues organs and systems in plants r1.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Different types of stele are: Vascular tissue is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, the main transport systems of plants. Although both xylem and phloem form a continuous tissue system throughout the plant body, the two tissues have different functions. The difference between xylem and phloem are as follows: The Leaf Vascular Tissue The VEINS made up of xylem and phloem which.
 Source: onlinebiologynotes.com
Source: onlinebiologynotes.com
What are the two types of vascular tissue in. What are the two types of vascular tissue? The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. Different types of stele are: Permanent tissue characteristics, types and functions Online Biology.
 Source: sciencephoto.com
Source: sciencephoto.com
The xylem is a complex tissue containing a range of cell types including: They are the conducting tissues that are responsible for the transport of water, mainly the xylem, while the transport of food in plants is done by the phloem tissue. Describe the function of each. What are the two types of vascular tissue? Vascular tissue in dicot plant stem, light microscopy Stock Video.
 Source: haikudeck.com
Source: haikudeck.com
Barclay, in pharmacognosy, 2017 4.1.4.1 vascular tissues. What are the two types of vascular tissue in. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. By berries emulous of fame grand (151k points) asked in biology jan 3, 2021 24 views. Plants by Lily Parker.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The tissue in vascular plants that circulates fluid and nutrients. Vascular tissue is important for the transportation of crucial substances within the plant. A vascular plant is any one of a number of plants with specialized vascular tissue. Peripheral vascular disease (pvd), commonly known as peripheral artery disease or pad is a blood circulation disorder of the arteries and veins situated away from your heart and brain. Vascular Tissue.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
It is majorly of two types: What are the 3 types of tissues found in vascular plants? Although both xylem and phloem form a continuous tissue system throughout the plant body, the two tissues have different functions. Xylem, which conducts water and nutrients up from the roots, and phloem, which distributes food from the leaves to other parts of the plant. PPT Cells and Tissues of the Plant Body PowerPoint Presentation ID.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. Different types of stele are: By berries emulous of fame grand (151k points) asked in biology jan 3, 2021 24 views. What are the two types of vascular tissue? Transport in plants 1.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
They typically occur together in vascular bundles in all plant organs, traversing roots, stems, and leaves. The 2 types of vascular tissues in plants are the xylem and phloem. Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves. Xylem is responsible for the transport of water and dissolved ions from the roots upwards through the. 11B06.2 CV3 Vascular Tissue System YouTube.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
They are the conducting tissues that are responsible for the transport of water, mainly the xylem, while the transport of food in plants is done by the phloem tissue. Xylem is responsible for the transport of water and dissolved ions from the roots upwards through the. The two types of vascular tissues xylem and phloem. The tissue in vascular plants that circulates fluid and nutrients. PPT Vascular Tissue Xylem and Phloem PowerPoint Presentation, free.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The 2 types of vascular tissues in plants are the xylem and phloem. Water and minerals are transported by. What are the two types of vascular tissue in plant? Describe the function of each. AS level. G.14 Distribution of vascular tissues in dicotyledonous.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Xylem is responsible for the transport of water and dissolved ions from the roots upwards through the. Plants are a kingdom of living organisms which can carry out carbon fixation. Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves. Xylem, which conducts water and nutrients up from the roots, and phloem, which distributes food from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Tissues organs and systems in plants r1.
 Source: temanku-uka.blogspot.com
Source: temanku-uka.blogspot.com
Vascular tissue is important for the transportation of crucial substances within the plant. Although both xylem and phloem form a continuous tissue system throughout the plant body, the two tissues have different functions. Vascular tissue is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, the main transport systems of plants. There are two kinds of vascular tissue: Vascular Tissue In Plants BIO 7 Preview for March 13 Plants.
Vascular Tissue Is Comprised Of The Xylem And The Phloem, The Main Transport Systems Of Plants.
Xylem, which conducts water and nutrients up from the roots, and phloem, which distributes food from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Xylem for water transport and phloem for transport of photosynthates. What are the 3 types of tissues found in vascular plants? What are the two types of vascular tissues?
It Is Majorly Of Two Types:
2.3 vascular tissues and cell types there are two vascular tissues in the vascular tissue system: The cells in vascular tissue are typically long and slender. The tissue in vascular plants that circulates fluid and nutrients. Barclay, in pharmacognosy, 2017 4.1.4.1 vascular tissues.
The Two Types Of Vascular Tissue Are Xylem And Phloem.
What are the two types of vascular tissue in plant? The 2 types of vascular tissues in plants are the xylem and phloem. Peripheral vascular disease (pvd), commonly known as peripheral artery disease or pad is a blood circulation disorder of the arteries and veins situated away from your heart and brain. Stele originated & evolved in pteridophytes.
It Is Made Up Of Two Different Kinds Of Tissues The Xylem And Phloem.
Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves. Dermal tissue covers the outer surface of herbaceous plants. There are two kinds of vascular tissue: Xylem tissue moved water and materials dissolved in it from roots to leaves.







